Different Types Of Qubits

Different Types Of Qubits A qubit (quantum bit) is a unit of quantum information that can exist in any superposition of a 0 and a 1 state, unlike a classical bit which can only be either 0 or 1. This allows qubits to hold more information than classical bits and to be used to perform complex calculations more quickly. Qubits are the fundamental building blocks of quantum computing, allowing quantum computers to be more powerful than classical computers. Scientists have crafted a range of qubits, from Neutral Atoms to NMR, NV center-in-diamond, photonic, superconducting, topological, and trapped ions. Here, we will provide a brief overview of each. A Neutral Atom qubit is a quantum computing system that uses neutral atoms as its qubits. A qubit is a quantum bit of information; neutral atoms store that information in this system. To create a Neutral Atom qubit, scientists must use laser cooling and optical trapping techniques to isolate neutral atoms in an ultra-high vacuum. This allows them to control the atoms and manipulate their internal states individually. Controlling and manipulating these atoms can create qubits representing quantum information. An NMR qubit is a type of qubit used in quantum computing that is based on Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR). It is made by using a small number of nuclear spins in a molecule, typically a few spins of protons or hydrogen, as the qubit. The nuclear spins of the molecule can be manipulated using magnetic fields and radio waves, allowing for complex operations to be performed. NMR qubits can be used to store and process information and are important building blocks for quantum computing. An NV center-in-diamond qubit is a type of qubit that uses a single nitrogen-vacancy center in a diamond lattice to store quantum information. It is made by implanting a nitrogen atom and a vacancy into the diamond lattice. The vacancy site is where the nitrogen atom would normally be located, resulting in a stable, negatively charged nitrogen-vacancy center. The NV center is then further manipulated using lasers and microwaves to create a suitable qubit for quantum computing. A photonic qubit is a type of quantum bit used in quantum computing. It uses a photon, or a single particle of light, as the quantum information unit. Photonic qubits are created by trapping single photons in cavities, using a laser to generate the photons and a beam splitter to guide them into the cavity. The photons can also be manipulated using refractive and reflective elements, allowing them to be used as the basis for quantum algorithms. Photonic qubits are faster, more reliable, and more stable than other types of qubits, making them attractive for quantum computing applications. A superconducting qubit is a type of quantum bit that uses superconducting electrical circuits to store and process quantum information. Superconducting qubits are made by controlling the interaction between two or more quantum objects, such as photons or electrons, that are confined in a superconducting circuit. The interactions between these objects are manipulated using electrical signals, which can be used to control the quantum state of the qubit. Superconducting qubits are often referred to as “artificial atoms” because they exhibit many of the same properties as real atoms. A topological qubit is a type of quantum bit that is created by encoding information into the structure of a physical system. It has the potential to be much more stable, reliable, and fault-tolerant than other types of qubits, making it an important part of quantum computing research. Topological qubits are made by manipulating the properties of the physical system, such as the electric or magnetic fields, to create a topologically protected qubit. This protection helps reduce external noise’s effects on the qubit, allowing for longer-term storage and manipulation of quantum information. For detailed information about this type of qubit, you can review my blog on Topological qubits. A trapped-ion qubit is a form of quantum computing that uses ions as the building blocks of quantum information. The ions are held in a vacuum within a trap, which is usually an electromagnetic trap. The ions are then entangled with one another and manipulated using laser pulses. This enables the execution of quantum operations, such as quantum logic gates, on the ions. This type of quantum computing is advantageous because the ions can be held for a long time and the interactions between them are precisely controlled. Overall, trapped ion qubits offer an efficient and reliable way of performing quantum calculations. With each of these qubits boasting its own advantages and disadvantages, it is essential to understand the ins and outs of each in order to identify the best qubit for a given application. Neutral Atoms qubits, for example, are extremely reliable but require large amounts of hardware and cooling to be used. NMR qubits can be operated at room temperature but are prone to decoherence. NV center-in-diamond qubits are extremely robust and require minimal hardware; however, they are difficult to manufacture. Photonic qubits have the advantage of being able to transfer quantum data at long distances, but they are highly susceptible to decoherence. Superconducting qubits are relatively easy to set up and require minimal hardware; however, they are limited in the number of qubits that can be meaningfully operated together. Topological qubits are extremely robust, but they are difficult to manufacture. Finally, Trapped ion qubits are extremely reliable but require complex and expensive hardware. All of these qubits represent a huge step forward in quantum computing, and the future of the technology will depend heavily on the correct application of a suitable qubit. Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Email
Topological Qubits

Topological Qubits The reduced Planck constant, ħ, or Dirac constant, is the unit of particle spins and a fundamental physical constant that relates a particle’s energy to its angular momentum. It is denoted by the symbol ħ (h-bar). The reduced Planck constant is equal to the Planck constant divided by 2π. Its value is approximately 6.62607015 × 10−34 J⋅s. Bosons are particles that follow Bose-Einstein statistics and have integer spin (0, 1, 2, etc.). They are particles that can occupy the same quantum state and, as a result, can form Bose-Einstein condensates. Examples of bosons include photons and gluons. Fermions are particles that follow Fermi-Dirac statistics and have half-integer spin (1/2, 3/2, 5/2, etc.). They obey the Pauli Exclusion Principle, meaning that no two fermions can occupy the same quantum state. Examples of fermions include electrons, protons, and neutrons. While many researchers are working on building qubits with reasonable decoherence time, topological quantum qubits are a type of qubit constructed from a topological quantum system. They take advantage of the unique properties of anyone. An anyon is a 2-D quasiparticle that is neither a boson nor a fermion! Topological systems are systems whose properties are preserved under continuous deformations and are thus very stable against external disturbances. Topological quantum qubits are more resilient to errors than other qubits since they are not affected by local noise. This makes them ideal for use in quantum computing applications. Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Email
PennyLane As a Tool For ML

PennyLane As a Tool For Quantum ML PennyLane is a quantum computing platform developed by Xanadu, a quantum computing company, to help organizations explore and leverage the power of quantum computing. It enables the use of quantum computers, simulators, and quantum machine learning algorithms in an easy-to-use and intuitive environment. PennyLane is an open-source platform that provides a comprehensive set of features and tools to help organizations develop and deploy quantum computing applications. Recently, PennyLane has seen several advancements, such as the introduction of a new quantum programming language, PennyScript, support for the TensorFlow Quantum library, and integration with the popular machine learning library, PyTorch. With the introduction of PennyScript, developers are now able to easily create and run programs on the PennyLane platform while leveraging the power of quantum computing. This new language allows developers to write code more easily and quickly while also providing access to a range of quantum computing features and tools. In addition to the language, PennyLane has also introduced support for the TensorFlow Quantum library. This library provides a set of powerful tools for developing and deploying quantum machine learning applications. It enables developers to create models that can be used to analyze and predict quantum data, as well as allowing them to create and train machine learning models using the library. Finally, PennyLane has also integrated with the popular machine learning library, PyTorch. This integration allows developers to use PyTorch to create and train machine learning models using the power of quantum computing. This integration allows developers to leverage the power of both quantum computing and machine learning, enabling them to create more powerful and accurate models. Overall, PennyLane has seen several advancements in recent times, allowing developers to easily create and run programs on the platform while leveraging the power of quantum computing. With the introduction of PennyScript, support for the TensorFlow Quantum library, and integration with PyTorch, PennyLane is becoming an increasingly popular platform for quantum computing applications. Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Email
TensorFlow Quantum Joins QML

TensorFlow Quantum joins QML TensorFlow Quantum is an open-source library created by Google to enable the development of quantum computing applications. It is built on top of TensorFlow, a popular deep-learning framework developed by Google. TensorFlow Quantum is designed to provide developers with a high-level interface to quantum computing hardware and simulate quantum systems. In recent years, TensorFlow Quantum has made significant advancements in the field of quantum computing. It has been used to develop quantum algorithms for a variety of applications, such as quantum machine learning, quantum circuit optimization, and quantum error correction. Furthermore, it has been used to develop quantum simulators and quantum computers. Furthermore, TensorFlow Quantum has made significant progress in quantum hardware as well. It is being used to develop quantum integrated circuits and quantum processors. It has also enabled the development of quantum-safe encryption algorithms, which can be used to secure communications and data. Finally, TensorFlow Quantum is being used to develop quantum computing applications for various industries. It has been used to develop applications for finance, healthcare, and other industries. It has also enabled the development of quantum computing-based solutions for various scientific and industrial applications. These advancements demonstrate the potential of TensorFlow Quantum to make a significant impact on the development of quantum computing applications in the near future. Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Email
What Is Quantum Computing?
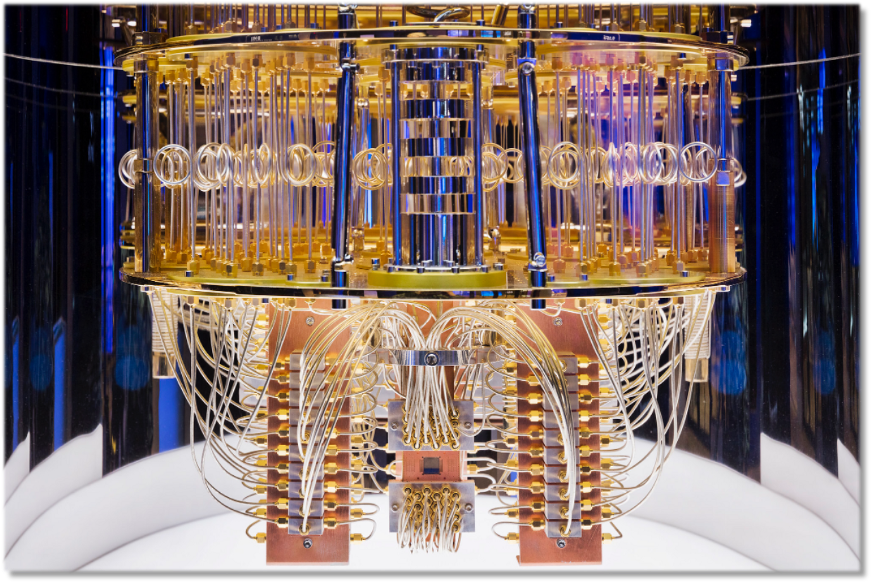
What is quantum computing? Quantum computing is a relatively new computing technology that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to solve complex computational tasks. It has the potential to revolutionize the way computers are used, allowing them to process information faster and more efficiently than ever before. Quantum computers use qubits, which are particles that can exist in a state of superposition, allowing them to process information simultaneously. This means that a quantum computer can solve problems that would take a traditional computer an impossible amount of time. Quantum computers have the potential to solve problems that are far beyond the capabilities of traditional computers, such as machine learning, artificial intelligence, and cryptography. They could be used to simulate complex chemical reactions, allowing scientists to develop new materials and drugs more quickly and efficiently. In addition, they could be used to solve optimization problems, such as those related to logistics, finance, and energy management. The development of quantum computing is an exciting and rapidly advancing field. It is still in its early stages, but researchers are making great strides in advancing the capabilities of quantum computers. In addition to advancing technology, researchers are also exploring ways to make quantum computing more accessible to the public. For instance, companies like Google and IBM are developing quantum computers that anyone with access to the internet can use. Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize the way we use computers and solve problems. It is a rapidly evolving field, and researchers are making great strides in advancing its capabilities. As technology continues to evolve, we will likely see more applications for quantum computing in the future. from qiskit.aqua.algorithms import QAOA from qiskit.aqua.components.optimizers import COBYLA # Define the problem problem = ExampleProblem() # Initialize the QAOA algorithm qaoa = QAOA(problem, COBYLA()) # Run the algorithm result = qaoa.run() # Get the optimal solution solution = result[‘optimal_solution’] Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Email
Quantum Computing In Industry
QUANTUM COMPUTING IN INDUSTRY Quantum computing is a rapidly evolving field of computing technology that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to manipulate and measure information. It has the potential to solve problems that are impossible to solve with traditional computing technologies. There are several different types of quantum computing, including gate-based quantum computing, adiabatic quantum computing, topological quantum computing, and optical quantum computing. Each type of quantum computing has its own unique advantages and disadvantages, so it is important to understand the differences between them in order to make the best decision for a given application. Here is a short list of potential problems that we could use the power of quantum computing in the industry: Back
ACTIVE RESEARCHES
ACTIVE RESEARCH Scientists and engineers are constantly finding new ways to leverage the power of quantum computing to solve complex problems and create innovative solutions. Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize the way we think about computing, and researchers are actively exploring new ways to use this technology to improve our lives. In terms of hardware, active research areas in quantum computing include: 1. Superconducting qubits: These are the most common type of qubits used in current quantum computers, and researchers are working to improve their coherence times and reduce errors. 2. Trapped ions: These qubits are highly stable and can be used to perform high-precision measurements, but they are more difficult to scale up. 3. Topological qubits: These qubits are based on topological materials’ properties and are considered highly fault-tolerant. You can find more information in the blog about this type of qubits. 4. Quantum dot qubits: These qubits are based on the electronic properties of semiconductors and have the potential for high-density integration. In terms of software, active research areas in quantum computing include: 1. Quantum algorithms: Researchers are working on developing new algorithms that can take advantage of the unique properties of quantum computers to solve problems faster than classical computers. 2. Error correction: Since quantum computers are highly susceptible to errors, researchers are working on ways to correct these errors and make quantum computers more reliable. 3. Quantum simulation: Researchers are using quantum computers to simulate the behavior of quantum systems, with applications in areas like materials science and chemistry. 4. Quantum machine learning: Researchers are working on using quantum computers to improve the performance of machine learning algorithms. 5. Quantum cryptography: Researchers are working on developing secure communication methods using quantum mechanics properties such as Quantum key distribution. Back
TYPES OF PROBLEMS
TYPES OF PROBLEMS Quantum computing is an emerging technology that has the potential to solve complex problems that are difficult or impossible to solve using traditional computing methods. Quantum computers can solve certain types of problems that classical computers cannot, such as quickly factoring large numbers (which is the basis for many modern encryption algorithms) and simulating quantum systems (which is essential in fields such as chemistry and materials science). They can also be used to speed up machine learning and optimization problems. However, it’s important to note that not all problems can be solved more efficiently on a quantum computer, and many critical practical applications for quantum computing are still being researched and developed. Some of the problems that can be solved using quantum computing include data analysis, drug discovery, optimization problems, cryptography, and quantum simulation. Quantum computing can also be applied to a variety of fields, such as finance, materials science, and artificial intelligence. By utilizing the power of quantum mechanics, quantum computing is able to unlock new levels of computing power and solve complex problems faster and more efficiently. Back
